CT-based deep learning radiomics analysis for evaluation of serosa invasion in advanced gastric cancer
Please click here to download the model.
Abstract
To develop and validate a deep learning radiomics model for evaluating serosa invasion in gastric cancer, a total of 572 gastric cancer patients were included in this study. Firstly, we retrospectively enrolled 428 consecutive patients (252 in the training set and 176 in the test set I) with pathological confirmed T3 or T4a. Subsequently, 144 patients who were clinically diagnosed cT3 or cT4a were prospectively allocated to the test set II. The contrast enhanced CT images of three phases were manually segmented. Conventional hand-crafted features and deep learning features were extracted based on CT images automatically and were utilized to build radiomics signatures via machine learning methods. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to develop a diagnostic model (radiomics nomogram) incorporating the radiomics signatures and subjective CT findings. In the experiments, the nomogram had powerful diagnostic ability in all training, test I and II sets with AUCs of 0.90 (95% CI, 0.86-0.94), 0.87 (95% CI, 0.82-0.92) and 0.90 (95% CI, 0.85-0.96) respectively.
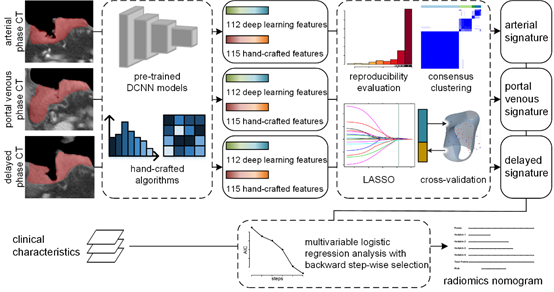
Figure 1. Radiomics modeling and analysis workflow.

Figure 2. Radiomics nomogram based on radiomics signatures and clinical characteristics.