Radiomics Profile
The fast evolution of medical imaging has fostered a comprehensive analysis method for medical images called radiomics. Radiomics generally refers to the extraction and analysis of large amounts of advanced quantitative imaging features with high throughput from medical images obtained using CT, PET or MRI. In comparison with the traditional practice of treating medical images as pictures intended solely for visual inspection, the aim of radiomics’ analysis is the transformation of medical images into minable data combined with other patient clinical information. Using sophisticated bioinformatics tools, researchers are able to develop models that may potentially improve diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive accuracy.
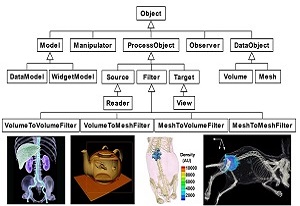
MITK (Medical Imaging ToolKit)
MITK, standing for Medical Imaging ToolKit, is a C++ library for integrated medical image processing and analyzing developed by Dr.Tian and his team of CASMI. It provides a consistent framework combining the functions of image reconstruction, segmentation, registration and visualization to medical imaging society. MITK is a new option for medical imaging society in terms of research and education aspects and is free for download.
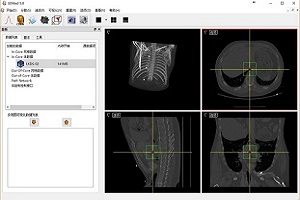
3DMed (3D Medical Image Processing and Analyzing System)
3DMed is formed by some kernel modules that define a plugin style programming interface and a series of loosely coupled plugins that implement different kinds of functions. These make 3DMed not only suitable for the development and validation of algorithms, but also very easy to be customized for a given purpose. 3DMed is an open source project and is free for download.
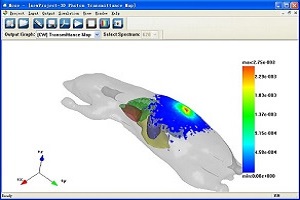
MOSE (Molecular Optical Simulation Environment)
MOSE is a simulation platform for bioluminescence imaging research. MOSE is featured by that it implements the simulation of light propagation both in tissues with complicated shapes and in free-space. The powerful visualization abilities facilitate the simulation and data analysis easily. MOSE is provided as freeware for research and educational institutions.
Radiomic Software Promotion
Radiomics Software is a computer assisted tumor analysis software. Given a tumor image, this software segment tumor and extract tumor features automatically. Afterwards, intelligent models trained with big medical image data can classify and diagnose tumor. This software has been applied in more than 30 third-grade class-A hospitals and is free for download in terms of research and education.
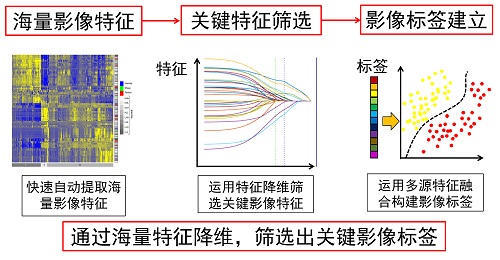
RIPM (Radiomics Individual Predication Models)
Based on numerous clinical images combined with engineering methods and clinical diagnostic experience, the aim of radiomics is to create a scientific, quantitative, and large data-driven analysis model for tumor prognosis, and then apply it to clinically aided diagnosis. More and more radiomic models from researchers in CASMI are contributed to this platform.
Members
Please click here to entry pages for team building about Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Connect Us
- Address: 95 Zhongguancun East Road, 100190, BEIJING, CHINA.
- Tel: +86-010-82618465
- Email: mitk@radiomics.cn
- Web site: www.3dmed.net
- WeChat:
-